Medical Scribe Roles Increasingly Essential in Emergency Departments
Emergency departments (EDs) are under relentless pressure—overflow, documentation drag, clinical burnout, and revenue leakage collide every shift. High-functioning medical scribes solve the bottlenecks that software alone hasn’t fixed: real-time documentation, coding clarity, and throughput discipline that cuts door-to-doc times and reduces LWBS. In this guide, you’ll see exactly how EDs deploy scribes to reclaim minutes, protect revenue, and strengthen compliance—plus the staffing models, QA routines, and training tracks that separate average programs from top-quartile EDs.
Scribes are no longer a “nice to have.” They’re a throughput and revenue infrastructure layer—tied directly to coding accuracy, audit readiness, and clinician bandwidth when every second matters.
1) Why EDs Are Doubling Down on Scribes Right Now
ED leaders aren’t hiring scribes for note-taking; they’re buying measurable operational lift across documentation quality, coding specificity, and patient flow. A well-run scribe program prevents documentation slippage during volume spikes, preserves E/M level integrity, and creates the conditions for safer handoffs and faster dispositions.
Coding certainty in chaos. In fast-moving encounters, scribes capture ROS, HPI, MDM, procedures, and critical care time with the granularity coders need—backed by billing-code updates and audit-proof structure. See policy shifts and code impacts in: CMS guideline changes, billing-code changes, HIPAA 2025 updates, and our Medical Scribe hub: ED scribe resources.
MDM that defends your level. Scribes prompt for differentials, diagnostic rationale, social determinants, and risk so MDM tells a defensible clinical story. To bulletproof documentation, pair with: ICD-10 quick mapping, billing basics, top billing errors to avoid, and chart-audit mastery.
Throughput & LWBS reduction. By keeping clinicians in front of patients, scribes protect throughput KPIs and reduce left-without-being-seen. Blend with: schedule optimization techniques, EMR data-entry steps for admins, urgent care hiring map, and scribe template libraries.
Compliance that scales. EDs are high-risk for HIPAA lapses and security drift. Scribes trained on privacy, minimum necessary, workstation hygiene, and dictation tools (see: HIPAA essentials guide, EMR security best practices, voice & dictation tools, and major provider hiring trends) keep EDs audit-ready.
ED Failure Points — Scribe Interventions — Measurable Wins
| Failure Point | Targeted Scribe Intervention | Operational/Financial Win |
|---|---|---|
| Inconsistent HPI detail | Structured HPI prompts; capture onset, quality, modifiers | Defensible MDM; higher E/M specificity |
| Missed critical care time | Timestamp tracking; confirm interventions & responses | Prevents revenue loss on high-acuity cases |
| Fragmented ROS/PE | Complaint-aligned ROS/PE templates | Cleaner audits; coding accuracy |
| Delayed orders & results trail | Live order→result checklist; re-eval ticklers | Shorter LOS; faster dispo decisions |
| MDM lacks risk elements | Risk/DI prompts, alternatives, shared decision-making | Appropriate level selection; audit safety |
| Procedures under-documented | Consent, anesthesia, technique, device, complications checklist | Procedure revenue preserved |
| Poor handoff notes | Concise ED course & sign-out summaries | Safer transitions; fewer repeats |
| Inaccurate discharge diagnosis | ICD-10 cross-check; coder liaison | Cleaner claims; fewer denials |
| Voice-to-text errors | VR tool curation; error correction workflow | Time savings; fewer edits |
| HIPAA exposure in pods | Screen privacy positioning; minimum-necessary discipline | Risk mitigation; audit readiness |
| LWBS during volume spikes | Provider face-time protection; intake scripting | Lower LWBS; revenue retention |
| Template overuse | Complaint-specific templates + free-text where it matters | Clinical accuracy; coder confidence |
| Untracked re-evaluations | Time-stamped updates & response to therapy | MDM clarity; denial defense |
| Order/result mismatch | Closed-loop verification before dispo | Fewer callbacks; safer discharges |
| CPT misses on procedures | Procedure pick-list; coder sync | Complete charge capture |
| Incomplete allergy/medication history | Structured med rec prompts; pharmacy cross-check | Safety; fewer adverse events |
| Sepsis bundle timing gaps | Clock-start capture; bundle step checklists | Core measure compliance; outcomes gain |
| Stroke door-to-needle delays | Code stroke timestamps; imaging & tPA criteria notes | Reduced time metrics; quality score up |
| Boarding documentation drifts | Periodic condition updates; ongoing orders tracked | Continuity; safer boarding |
| Social determinants not captured | SDOH prompts; barriers & resources recorded | Care plan relevance; risk documentation |
| Interpreter use not documented | Interpreter ID, language, method logged | Compliance; informed consent defense |
| Restraint documentation incomplete | Indication, monitoring, release time | Regulatory adherence; risk reduction |
| Critical care elements not itemized | Time in/out; qualifying activities enumerated | Accurate CC capture; revenue protection |
| Consult recommendations not incorporated | Consult time & rec summary added to MDM | Liability reduction; audit clarity |
| Discharge instructions lack clarity | Plain-language summary; return precautions | Fewer callbacks; improved safety |
2) High-Impact ED Scribe Tasks from Triage to Dispo
Triage augmentation. Scribes align chief complaint, acuity, vitals, and past history so the clinician’s initial impression maps cleanly to ICD-10 and MDM. Pair with: ICD-10 guide, EMR data-entry steps, schedule optimization, and HIPAA essentials.
HPI precision. Scribes prompt for OPQRST, context, associated symptoms, red flags, and prior attempts at care. Lock it with: MDM-supporting templates, billing basics, billing-code updates, and provider hiring trends.
ROS/PE balance. Avoid “template bloat” without missing essentials. Integrate complaint-specific PE. See: chart-audit mastery, top billing errors, EMR security best practices, and voice/dictation tools.
Orders & results tracking. Scribes maintain a live checklist linking orders to results, flagging abnormals and timing re-evals. Reinforce with: daily schedule tactics, urgent-care hiring map, template libraries, and HIPAA 2025 key changes.
MDM clarity. Capture differentials, data reviewed, risk discussion, shared decision-making, social barriers, and dispo rationale. Support with: CMS guideline changes, coding changes impact, billing errors to avoid, and billing foundations.
Procedure documentation. Scribes run checklists: consent, indication, anesthesia, technique, device, complications, and tolerance. Tighten with: template libraries, ICD-10 mapping, chart audits, and HIPAA essentials.
Re-evaluation timestamps. Track response to therapy and evolving risk, supporting level selection and safety. Align with: billing basics, coding changes, EMR security, and HIPAA 2025 updates.
Discharge accuracy. Cross-check ICD-10, reconcile orders, document return precautions, and ensure patient-friendly summaries. Pair with: ICD-10 guide, common billing errors, audit mastery, and HIPAA essentials.
3) The ROI Math ED Leaders Care About (Modeled, Practical, Defensible)
Time back to providers. Even a conservative 6–10 minutes saved per encounter can move a high-volume ED from gridlock to flow. Reclaiming physician minutes converts directly to additional completed encounters and fewer LWBS. Anchor the ops design with: schedule optimization, EMR data discipline, provider hiring trends, and urgent-care hiring directory.
Revenue preservation through accurate coding. When MDM risk, procedures, and critical care are fully documented, EDs protect level selection and charge capture. Bolster this with: billing basics, billing-code change alerts, avoidable billing errors, and template libraries.
Denied claim reduction. Denials often trace back to documentation defects. Scribe-driven checklists at dispo verify ICD-10 alignment, procedure completeness, and order/result closure. Reinforce with: ICD-10 companion, chart audit process, EMR security practices, and HIPAA essentials.
Burnout mitigation and retention. Offloading clicks, scrolling, and hunting data keeps clinicians fresher and safer. Layer with voice tech choices and templates: dictation tools guide, template mega-guide, ED scribe hub, and HIPAA 2025 updates.
Which Telehealth Challenge Impacts Your Workflow Most?
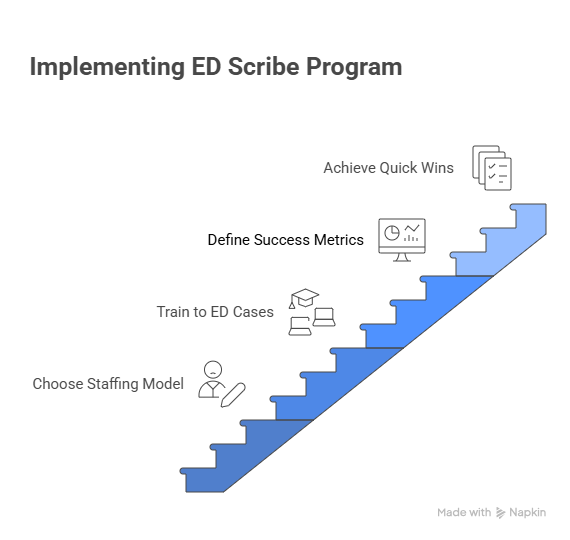
4) Implementing an ED Scribe Program: Models, QA, and Day-1 Wins
Choose the right staffing model.
In-house hires give culture fit and schedule control—pair with training libraries and HIPAA refreshers: template mega-guide, HIPAA essentials, EMR security, and voice/dictation options.
Vendor-managed scribes accelerate startup and QA; validate with SLA metrics tied to chart-closure times and MDM completeness. See: major provider hiring trends, ED scribe hub, billing-code changes, and HIPAA 2025 updates.
Hybrid/on-site + virtual keeps coverage 24/7 at balanced cost; use role routing so on-site scribes handle critical care/trauma bays while virtual scribes manage lower-acuity pods. Reinforce with: urgent-care hiring map, template libraries, ICD-10 mapping, and EMR data-entry steps.
Train to ED cases, not theory. Build micro-modules: chest pain, stroke, sepsis, pediatric fever, laceration, ortho injuries, behavioral health, OB emergencies. Each module includes MDM prompts, procedure checklists, and ICD-10 shortlists. Stock the curriculum from: template mega-guide, ICD-10 guide, billing basics, and HIPAA essentials.
Define success metrics up front. Track chart-closure time, MDM completeness rate, procedures coded vs. performed, critical care capture, E/M level shifts, denial rates, provider minutes saved, and LWBS. Reinforce the monitoring with: chart-audit mastery, top billing errors, billing-code changes, and EMR security.
Day-1 quick wins.
Deploy ED-specific templates for top 10 complaints. 2) Stand up a MDM “prompt pack.” 3) Add a procedure capture checklist to charge lag boards. Start with: templates, ICD-10 mapping, billing basics, and HIPAA essentials.
5) Building Talent Pipelines & Coverage You Can Actually Staff
Pre-med and gap-year routes. To scale coverage fast, partner with pre-med programs that funnel high-aptitude scribes for evenings/weekends. Source via: pre-med gap-year pipelines, healthcare recruiters & platforms, FQHCs hiring map, and the broader Medical Scribe resources.
Offshore/overnight support. When your ED needs 24/7 coverage, blend on-site scribes with vetted international teams for lower-acuity hours. Start with: international & offshore employers, recruiter directory, voice/dictation tools, and HIPAA 2025 updates.
Specialty-aligned float pools. Create scribe tiers for trauma, pediatrics, OB, psych, cardiac, and procedural bays. Build internal mobility into hospitalist night teams and urgent care partners using: hospitalist groups directory, peds/OBGYN networks, urgent care map, and template libraries.
Career ladders to retain talent. Scribes stay when they see growth: move from ED scribe → lead scribe → QA auditor → EMR super user → documentation educator → clinical research coordinator. Create bridges into CRO/SMO clinics with: clinical research sites list, recruiter platforms, FQHCs directory, and the Medical Scribe hub.
6) FAQs — Fast, Concrete, ED-Specific Answers
-
Track a pre/post bundle: chart-closure time, provider minutes saved/shift, MDM completeness rate, critical care capture, procedure charge capture, E/M level distribution, denial rate, and LWBS. Tie gains to billing-code changes and documentation: coding changes impact, billing basics, audit mastery, and template libraries.
-
Deploy 8–10 micro-modules by complaint (chest pain, stroke, sepsis, pediatric fever, laceration, ortho, OB, psych), plus HIPAA and EMR security refreshers. Use: HIPAA essentials, EMR security best practices, ICD-10 map, and templates.
-
Hybrid wins for many EDs: on-site scribes in trauma/resus and psych pods; virtual for lower acuity lanes and overnight. Balance cost with QA throughput using: voice/dictation guide, urgent-care hiring map, ED scribe hub, and HIPAA 2025 updates.
-
They document the clinical story that coders need—risk, data review, re-evals, procedures, and critical care time. Back it with: audit mastery, billing basics, top billing errors, and coding changes.
-
Show trends in charts closed <24h, MDM completeness rate, E/M level mix, critical care capture, procedure CPT completeness, denial rate, provider minutes saved/shift, and LWBS. Link to: schedule optimization, ICD-10 guide, EMR security, and template mega-guide.
-
By maintaining a closed-loop between orders, results, re-evals, and discharge, they reduce missed data and callback risk. Reinforce with: EMR data steps, chart audits, HIPAA essentials, and security best practices.