Step-by-Step Guide to Efficient EMR Data Entry for Medical Admins
Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) aren’t just a digitized version of paperwork—they’re the operational backbone of every modern healthcare system. But the efficiency, accuracy, and security of these records hinge on one role more than any other: the medical admin. From patient intake to compliance documentation, admins are the human checkpoint in a highly automated system. That means data entry isn’t a clerical task anymore—it’s a clinical safeguard.
In this guide, we break down step-by-step strategies for optimizing EMR data entry workflows. Whether you're handling intake at a front desk or supporting back-end billing and coding teams, every keystroke impacts patient care, audits, and claim accuracy. You’ll learn how to minimize errors, streamline repetitive tasks, and use automation tools wisely—while staying aligned with HIPAA and EMR compliance requirements. Let’s get to the part where your data entry transforms into operational excellence.
EMR Systems: A Quick Overview for Admins
Types of EMRs in Use Today
Not all EMR systems are created equal. While the core function—digitizing patient medical records—is standard, the features vary dramatically between platforms like Epic, Cerner, and Allscripts. Epic dominates large hospital networks, offering extensive customization and integration with labs and billing. Cerner, known for its data analytics, supports population health management. Smaller clinics often adopt Allscripts or athenahealth for ease of use and cost efficiency.
Understanding what EMR your facility uses is key to mastering navigation. Backend tools, search logic, and terminology tagging differ from one system to another. Admins must not only know where to input but also how data flows between departments, insurance modules, and patient access portals. Without this system literacy, data bottlenecks and duplicated entries become inevitable.
Why Admins Are Crucial to Data Flow
Medical admins are the bridge between clinical care and documentation. While providers may perform examinations and dictate notes, it’s the admin who ensures these notes are categorized correctly, coded, and linked to the right encounter. Misplaced data entries can delay treatment plans, trigger billing rejections, or lead to regulatory noncompliance.
Admins also control the chain of continuity—from verifying demographics to ensuring records are complete before claim submission. In many practices, they're responsible for following up on missing fields or flags in the EMR, effectively acting as data quality auditors in real time. This frontline data responsibility demands speed, precision, and ongoing system familiarity.
Preparing for Accurate EMR Entry
Patient Intake & Pre-entry Checks
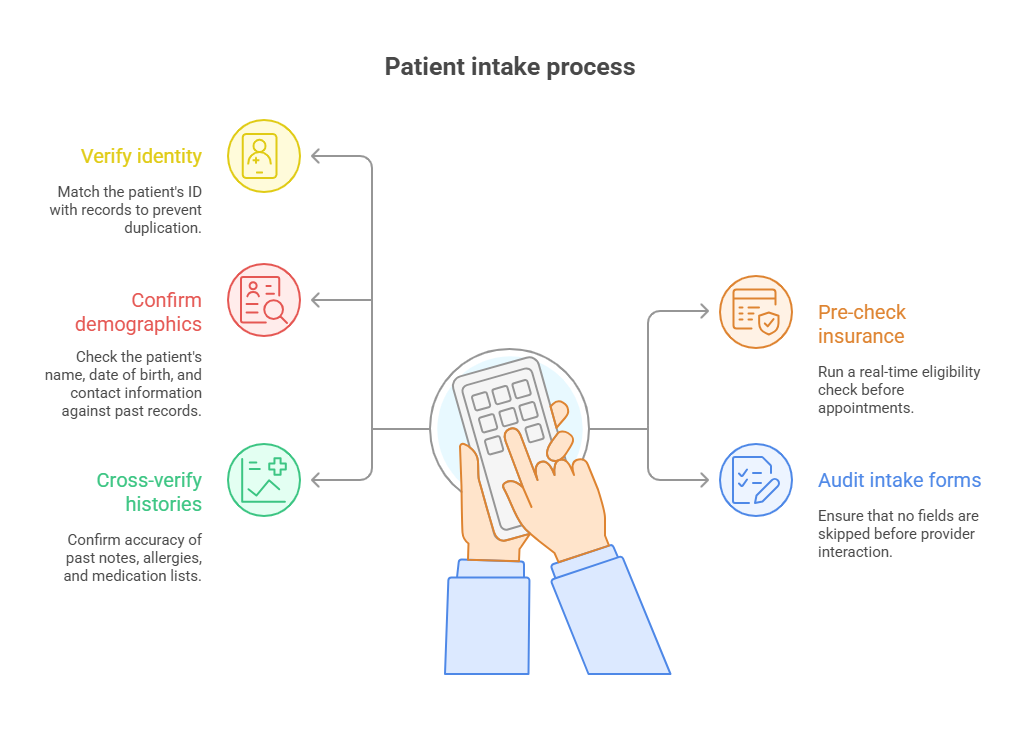
Accurate EMR data entry doesn’t begin at the keyboard—it starts at patient intake. Every form filled, ID scanned, and insurance verified lays the groundwork for accurate records. Admins must validate identity documents and cross-check demographic fields with existing records to prevent duplication. Even a minor discrepancy in birthdate or address can create redundant patient profiles and mess up longitudinal tracking.
One overlooked tactic is pre-verifying insurance before appointments. Many EMR systems integrate real-time eligibility checks—use them. Also, create a standardized checklist for verifying patient information. This should include spelling, date formats, allergy updates, and prior visit history. These checks avoid downstream errors that could impact provider workflows or billing outcomes.
Cross-verification Protocols
Mistakes in EMRs don’t just stem from data entry—they often come from unchecked assumptions. Admins should adopt a policy of "never trust, always verify" when transferring or updating sensitive data like medication histories or diagnoses. If a note seems auto-filled, confirm with the original entry or physician when in doubt. Don’t let interface convenience override accuracy.
Create a verification protocol: double-check spelling on clinical terms, verify time stamps, and confirm that all notes are logged under the correct provider and encounter type. For recurring patients, revalidate contact information every few visits. Having cross-verification protocols embedded into your daily workflow cuts down on errors and builds trust in the system's data integrity.
Best Practices in Real-Time EMR Entry
Reducing Typing Errors
The fastest way to wreck an EMR is by rushing through it. Speed is important, but accuracy must come first. Admins should always confirm spellings of medications, diagnoses, and provider names using internal search tools or quick-reference databases. Many EMRs flag unrecognized entries—use those red underlines as real-time warnings, not afterthoughts.
Avoid multitasking when entering patient data during high-volume hours. Break down workflows: complete one patient’s record fully before starting another to reduce cross-entry risks. Additionally, use read-back techniques—reading what you’ve entered out loud or silently—to catch typos before they propagate across multiple systems.
Auto-fill vs. Manual Entry Tradeoffs
Auto-fill fields can save time, but they're not foolproof. These features pull historical or templated data into current records, and if not updated, they carry outdated or incorrect information forward. Always validate what the auto-fill function imports before finalizing any entry.
Manual entry, while slower, forces attention. Use it when inputting critical details like patient complaints, medication lists, or surgical history. For templated progress notes, always update the subjective and objective sections per visit. Trust, but verify—auto-fill can never replace admin judgment.
| Best Practice | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Read-back entries | Reading what you've entered—aloud or silently—helps catch typos, missing words, and inconsistent data before saving. It’s especially useful for medications, dosages, and patient instructions that must be precise. |
| Avoid multitasking | Switching between patients or tasks mid-entry increases the chance of inputting the wrong data into the wrong chart. Single-task focus ensures that each patient’s EMR is accurate and complete. |
| Use EMR alerts | Most EMRs provide visual cues or alerts for missing fields, duplicated data, or incorrect formatting. Addressing these in real-time prevents administrative delays and billing rejections. |
| Segment entries by task | Break your data entry workflow into chunks—such as vitals, history, and provider notes. This keeps you organized, reduces mental fatigue, and allows for quicker cross-verification before saving. |
| Validate auto-fill content | Auto-fill pulls data from past entries and templates, which may be outdated or incorrect. Always confirm that imported content reflects the current visit to maintain clinical accuracy. |
Time-Saving Tools & Shortcuts
Learn your EMR system’s hotkeys, quick-entry codes, and smart text commands. These can reduce the number of keystrokes by up to 40% per patient record, according to internal hospital workflow studies. Shortcuts don’t compromise accuracy when used properly—they streamline routine notes, appointment scheduling, and referrals.
Set up your personal library of smart phrases (e.g., ".fup10" for “Follow-up in 10 days”) and custom templates for frequent scenarios like check-in, vitals logging, and lab ordering. Regularly update these shortcuts based on system changes or workflow shifts. When you invest time in configuring your tools up front, you gain hours back over the long term.
Voice-to-text Dictation Software
Dictation tools can reduce manual typing time dramatically, but they must be used with discretion and precision. Systems like Nuance Dragon Medical or built-in EMR voice modules are excellent for capturing physician notes, but they’re equally valuable for admins logging encounter summaries, referrals, or intake details. However, you must always edit after dictation—automated speech recognition has error rates up to 20% in noisy environments.
To optimize use, train your dictation software with your voice profile, update pronunciation settings, and use structured voice commands (“new paragraph,” “insert diagnosis”). Never use dictation in shared spaces without headsets or secure microphones to remain HIPAA-compliant and avoid eavesdropping risk.
Macros, Templates & Hotkeys
Macros and templates are your frontline defense against repetitive typing. Build templates for frequent appointment types (e.g., follow-ups, vaccinations, annual exams) and use conditional logic within those templates so only relevant fields populate. This avoids over-documentation and reduces cognitive fatigue during long shifts.
Most EMRs also allow custom macros for fields like insurance verification, pre-auth tracking, or no-show logs. For hotkeys, create a physical or digital cheat sheet. Map shortcuts for actions like "save and close," "jump to diagnosis," or "print encounter note" to your most-used keys. Once mastered, hotkey navigation cuts total EMR time by 15–30% depending on system.
To maintain speed without error, revisit and refine these shortcuts monthly. Outdated macros are just as dangerous as incorrect data—they introduce lazy habits and compromise accuracy.
| Tool | Description | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Hotkeys | Custom keyboard shortcuts that allow quick access to common EMR functions such as saving a chart, opening patient history, or launching lab orders. | Reduces navigation time by 15–30% and minimizes mouse usage, leading to smoother workflows during peak hours. |
| Smart Phrases / Macros | Short character codes (e.g., ".fup7") that expand into complete sentences or phrases for common documentation entries like follow-up instructions. | Speeds up charting by automating repetitive text blocks, cutting total typing time by up to 40% per patient. |
| Voice Dictation | Speech-to-text tools integrated with EMRs or external software (e.g., Dragon Medical) for real-time documentation of provider notes and admin input. | Eliminates manual typing for long-form text, especially useful in fast-paced clinics; improves documentation completeness. |
| Pre-built Templates | Reusable note structures for specific visit types like annual exams or follow-ups, often including auto-populated fields and logic-based customization. | Standardizes documentation across similar encounters while reducing redundancy and lowering the risk of missing required fields. |
| Dashboard Alerts | System notifications that display incomplete charts, unsigned notes, or data inconsistencies requiring follow-up. | Improves task tracking and reduces the chance of delayed billing or compliance issues due to unaddressed entries. |
Error Handling, Audits & Data Protection
Correcting Mistakes & Audit Trail Use
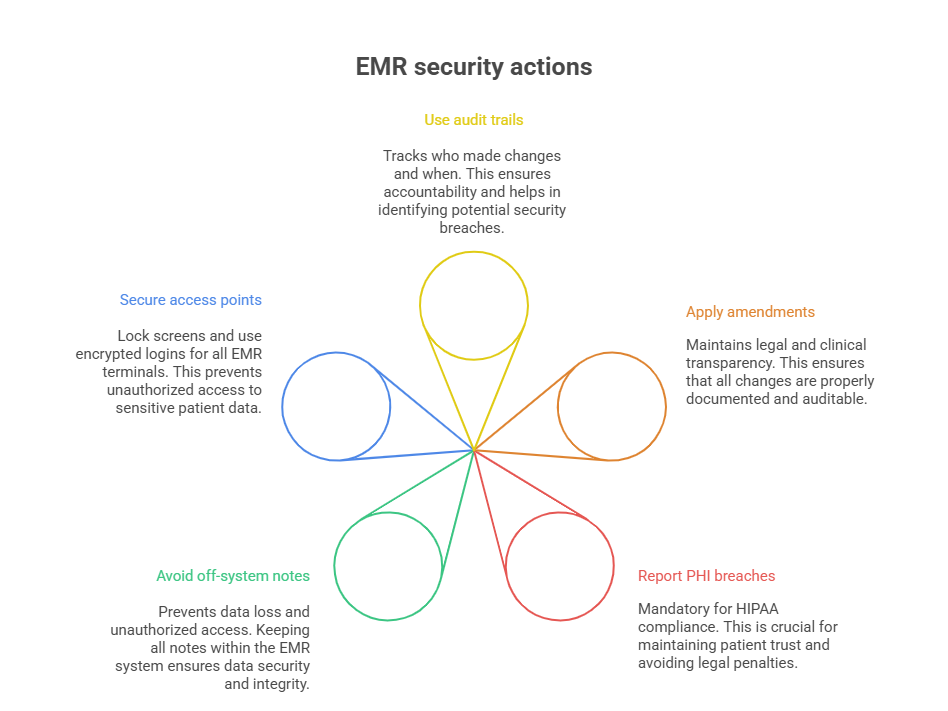
Every EMR input leaves a trace, and admins must treat error correction as a compliance-sensitive task, not a casual edit. Never delete entries or overwrite them without understanding the system’s audit trail. Most platforms track changes by user ID, timestamp, and original content, ensuring accountability. To correct a mistake, use the system’s built-in amendment or addendum functions, which preserve historical accuracy while updating the clinical record.
For time-sensitive entries—such as misfiled lab results or incorrect visit summaries—flag the entry and notify the appropriate provider or supervisor immediately. When admins correct documentation swiftly and transparently, they reduce downstream risk for both billing and care continuity.
Train yourself to recognize system flags. Many EMRs alert you to missing required fields or discrepancies across forms. Rather than ignoring these, treat them as early warning signs of bigger data issues.
HIPAA-Compliant Handling of Errors
Data entry isn’t just about speed—it’s a compliance minefield. Any error that involves Protected Health Information (PHI) must be corrected in a HIPAA-compliant manner. This means never sharing screenshots or printing incorrect data unless it’s part of a formal correction process. All edits must occur within the secure EMR environment, using traceable workflows.
If a breach or unauthorized disclosure occurs—even unintentionally—it must be documented and escalated according to your organization’s privacy protocol. Many breaches start with simple mistakes: sending patient data to the wrong provider inbox or misclicking a referral dropdown. Build habits that eliminate casual exposure, like locking screens during breaks and never leaving notes unsaved on shared computers.
Admins must also avoid storing PHI outside EMR systems. Don’t jot sensitive info on paper sticky notes or unsecured spreadsheets. If it’s not encrypted and trackable, it’s not compliant.
Why Take Our Medical Scribe Certification
Medical admins and scribes are no longer just support staff—they’re documentation specialists, workflow optimizers, and compliance gatekeepers. The Medical Scribe Certification by ACMSO is built to equip professionals with exactly the tools they need to excel in fast-paced, EMR-heavy clinical settings. If you're entering or advancing in the healthcare field, this is the certification that translates directly into employable skills.
The program covers everything from medical terminology and clinical note structure to hands-on EMR simulation training. You'll learn to work within real system environments, identify common input errors, and apply data protection protocols that align with HIPAA and 21 CFR Part 11 standards. Unlike other generalist programs, ACMSO’s certification focuses squarely on the role of the modern scribe and admin—where documentation meets efficiency.
Modules also include real-time scribing for physicians, template usage, insurance and billing coordination, and high-volume chart management. Each segment is structured to reflect actual workflows, so graduates don’t just know the theory—they’re job-ready from day one. You'll even gain strategies to minimize audit risks and maintain data integrity under pressure.
Most importantly, this certification reflects current industry hiring trends. Clinics, hospitals, and telehealth providers increasingly prefer scribe candidates who are pre-trained on EMR protocols. By earning the Medical Scribe Certification by ACMSO, you're not just getting a credential—you're positioning yourself for frontline roles in documentation, pre-authorization, and provider support.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
The most efficient EMR data entry method combines smart navigation, automation tools, and process discipline. Start with pre-entry checks during intake—accurate initial data avoids correction later. Use hotkeys, templates, and voice-to-text for speed, but always verify content before submission. Break entries into blocks (e.g., vitals, history, diagnostics) and complete one section fully before moving on. Avoid multitasking, as it leads to cross-record mistakes. For repeat visit types, set up reusable templates tailored to the provider’s preferences. And if your EMR has integrated alerts or red flags, use them to catch missing fields in real time. Speed matters, but error-free completion saves the most time long-term.
-
Most mistakes happen during rushed input, distracted multitasking, or improper use of auto-fill tools. To avoid this, admins should standardize pre-entry verification, including confirming name spellings, insurance data, and date of birth. Use the EMR's audit trails and system alerts to detect inconsistencies. For manual entry, break text into structured fields to improve focus and accuracy. Don’t rely on memory—refer to verified documentation or real-time provider input. Create a daily cross-check checklist for frequent data types like medications or allergies. Finally, admins should regularly review training from the Medical Scribe Certification by ACMSO, which teaches real-world correction and validation techniques.
-
Voice-to-text tools like Dragon Medical One or EMR-integrated dictation modules are highly efficient—but only when used correctly. They're ideal for longer sections like encounter summaries or provider comments. However, noisy environments and poor pronunciation often introduce transcription errors. Always review and edit dictations immediately after input. Use voice commands like "new paragraph" or "insert diagnosis" for better structure. Avoid using dictation for fields requiring exact phrasing, like medication dosage or billing codes. Most importantly, only use these tools on secure, HIPAA-compliant systems with encrypted microphones, especially in shared spaces. Dictation boosts speed, but unchecked voice input can compromise compliance.
-
The Medical Scribe Certification by ACMSO is specifically designed to train individuals for real-world documentation and EMR entry roles. It includes modules on electronic charting, structured note composition, EMR navigation, and HIPAA-compliant documentation practices. Students get exposure to simulation-based data entry tasks, which mirror what’s expected in clinics, hospitals, and telehealth environments. The curriculum also covers communication protocols with providers, accuracy during live scribing, and system-specific navigation tools. In short, it turns theoretical knowledge into actionable workflow skills. Graduates are equipped to hit the ground running as entry-level scribes or administrative support professionals in EMR-intensive healthcare settings.
-
Yes, but only with discipline and regular updates. Templates reduce typing and ensure consistency, but when left unmodified, they often carry forward outdated or incorrect information. Always review the default text before applying it. Use conditionally formatted fields to customize templates per visit type, provider, or specialty. Make sure subjective and objective fields reflect the current encounter—not just previous data. For new admins, building your own library of templates based on actual workflow will create a safer starting point. Training programs like the Medical Scribe Certification by ACMSO also include instruction on how to safely customize and use EMR templates.
-
Several tools help reduce manual workload without compromising accuracy. Hotkeys let you navigate and input faster—learn system-specific commands for actions like saving, searching, or inserting codes. Smart text phrases and macros let you expand short commands (e.g., ".followup") into full sentences. Voice dictation accelerates long-form notes, while templates streamline repetitive encounters like wellness exams or vaccine entries. Admin dashboards also help track incomplete fields, missing labs, or unsigned notes across patients. But none of these are plug-and-play—they require admin setup and discipline. Courses like the Medical Scribe Certification by ACMSO train users to build and optimize these tools.
-
EMR systems log every user action through an audit trail—a backend log that records what was entered, changed, or deleted, by whom, and when. These logs are vital during billing reviews, malpractice claims, or HIPAA investigations. Admins must use correction tools properly—never delete data or backdate entries. Instead, use amendment or addendum options that maintain transparency. Regularly review audit alerts, especially if the system flags repeated access to sensitive data or inconsistent entry times. Knowing how to navigate these trails, and how to correct errors compliantly, is a skill taught in the Medical Scribe Certification by ACMSO.
-
Healthcare systems are increasingly reliant on certified medical scribes to reduce physician workload and improve EMR accuracy. With rising demand for compliant, efficient documentation, the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects above-average growth in medical admin support roles. Employers prefer candidates who can start without on-the-job EMR training, especially in outpatient, urgent care, and telemedicine settings. Certification from ACMSO signals that you're trained in documentation protocols, HIPAA compliance, and real-time scribing under pressure. Graduates often land roles as scribe-specialists, charting assistants, or EMR documentation officers—giving them a major edge in both clinical and non-clinical hiring tracks.
The Take Away
Efficient EMR data entry isn’t just about speed—it’s about precision, compliance, and real-time clinical impact. As a medical admin or aspiring scribe, your role directly affects billing accuracy, provider efficiency, and patient safety. Every field you complete, every correction you make, and every shortcut you use plays into a larger system of accountability.
If you're serious about mastering EMR workflows and stepping into a high-demand healthcare support role, the Medical Scribe Certification by ACMSO gives you the structured, hands-on training to make it happen. You’ll gain tools, protocols, and system mastery that employers are actively looking for right now.
Stop guessing your way through documentation. Get certified. Get confident. Get hired.