CMS Announces Changes in Billing Codes: Immediate Impact on CMAAs
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has announced one of its most extensive billing code reforms in over a decade, reshaping the administrative backbone of U.S. healthcare. From outpatient claims to telehealth billing and AI-assisted documentation, these changes will immediately impact Certified Medical Administrative Assistants (CMAAs) — the professionals responsible for ensuring that every charge, modifier, and patient record aligns with federal standards.
The update isn’t just a coding refresh; it’s a shift in how healthcare organizations handle data integrity, audit traceability, and revenue cycle management. For hospitals, it’s a compliance challenge. For CMAAs, it’s an opportunity to prove their strategic value within the administrative hierarchy.
According to the ACMSO Administrative Workforce Report, over 78% of healthcare providers are re-evaluating their internal billing processes to meet the new CMS framework. Certified professionals are leading this transition — equipped with the literacy to manage new modifiers, integrate hybrid telehealth rules, and cross-verify claims within EHR systems.
1. Understanding the 2025 CMS Billing Code Overhaul
CMS’s 2025 billing update introduces new Evaluation and Management (E/M) categories, expands telehealth reimbursement, and redefines how time and AI are factored into claim approvals.
Key updates include:
Consolidation of E/M service levels 1–3 to streamline outpatient documentation.
Expansion of telehealth visit codes, covering asynchronous (non-live) consultations.
Introduction of AI verification codes for machine-generated clinical documentation.
Time-based billing now includes administrative review periods.
Reinforcement of audit traceability protocols across multi-system EMRs.
In the words of CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure, “The 2025 reform emphasizes transparency and accountability, not just speed.”
While clinical accuracy has always been the foundation of billing, this reform acknowledges that administrative accuracy is equally crucial. CMAAs — who bridge clinical and clerical workflows — now have expanded authority to interpret and validate digital documentation for billing submission.
CMS is also aligning its structure with ICD-11, requiring staff to maintain dual-coding proficiency during the transitional phase. That’s where certified assistants with ICD-11 readiness training stand out, ensuring no data loss or miscoding occurs.
2025 CMS Billing Code Updates — Administrative Impact Summary
| Update Area | Description | Impact on CMAAs |
|---|---|---|
| E/M Code Consolidation | Merged levels 1–3 outpatient visit codes. | Simplifies reporting but heightens documentation precision. |
| AI-Assisted Documentation | New codes for AI-reviewed notes. | Requires human validation before CMS submission. |
| Telehealth Reimbursement | Expanded hybrid visit coverage. | CMAAs verify dual authentication for remote patients. |
| Time-Based Billing | Includes administrative and clinical review. | CMAAs document every minute with timestamp accuracy. |
| Audit Traceability Policy | Mandates cross-platform log synchronization. | Assistants manage digital trace validation reports. |
| Modifier 25 Review | Stricter oversight for same-day procedures. | Demands precise contextual documentation by CMAAs. |
| Modifier 95 Update | New sub-conditions for telehealth billing. | Requires workflow revision in EMR billing modules. |
| ICD-11 Transition | Hybrid support for ICD-10 and ICD-11. | Assistants maintain cross-coding fluency. |
| Cross-State Compliance | Uniform federal standards introduced. | Certification enhances employability nationwide. |
| Prolonged Services Codes | Broader inclusion of non-face-to-face time. | CMAAs account for administrative review minutes. |
| Appeal Documentation | Revised tracking for denied claims. | Facilitates accurate audit reconciliation. |
| Education Alignment | New CMS training compliance requirement. | Increases demand for ACMSO-certified CMAAs. |
| Bundled Care Codes | Broadened chronic care bundles. | CMAAs manage inter-departmental claim linkage. |
| Data Transparency Act | New disclosure regulations. | Assistants provide accurate patient cost summaries. |
| AI Verification Codes | Identifiers for automated documentation. | CMAAs tag AI-generated records for review. |
| Training Mandate | Annual competency revalidation required. | Boosts continuous learning via ACMSO modules. |
| Digital Consent Logs | E-consent required before billing submission. | CMAAs maintain audit-ready consent archives. |
| Remote Monitoring Codes | Expanded billing for device-based tracking. | Assistants verify transmission integrity and reporting. |
| AI Audit Alignment | New tagging structure for ML-driven claims. | Requires CMAA oversight in algorithmic billing. |
2. How the Changes Affect Daily CMAA Workflows
For Certified Medical Administrative Assistants, these reforms mean restructured responsibilities. Data accuracy, time validation, and audit traceability are now daily expectations rather than periodic checks.
CMAAs will spend more time:
Cross-checking encounter documentation against billing timelines.
Verifying AI-augmented entries for modifier accuracy.
Managing interdepartmental communication through Patient Management Systems.
Ensuring all submissions meet HIPAA–CMS privacy convergence policies.
According to the ACMSO Medical Billing Software Glossary, these updates particularly affect hybrid clinics that combine in-person and telehealth services — both must now meet identical billing integrity standards.
As one administrative supervisor at Mercy Hospital stated, “We’re not just processing codes anymore — we’re interpreting them.”
3. Preparing for Compliance: Steps for CMAAs
To keep pace, CMAAs should follow a structured adaptation roadmap:
Complete Continuing Education: Enroll in ACMSO’s CMAA Compliance Training, updated quarterly with CMS modules.
Implement Real-Time Validation: Integrate AI-assisted audit flags directly into billing workflows.
Leverage Cross-System Tools: Use EMR Interoperability Guides for multi-department consistency.
Audit Readiness Simulations: Conduct dry runs to pre-identify compliance vulnerabilities.
Track Modifier Use: Master modifier 25, 59, 95, and their cross-conditional logic.
With proper training, CMAAs can reduce claim rejection rates by up to 36%, as noted in ACMSO’s 2025 audit projections.
Which New CMS Billing Area Challenges You Most?
4. Why Certification Is Now Non-Negotiable
Certification is no longer optional; it’s a compliance shield. With CMS expecting fully trained personnel to manage billing workflows, uncertified staff pose a quantifiable risk.
The ACMSO Certified Medical Administrative Assistant Program prepares professionals to interpret modifiers, track AI documentation, and generate compliant billing reports.
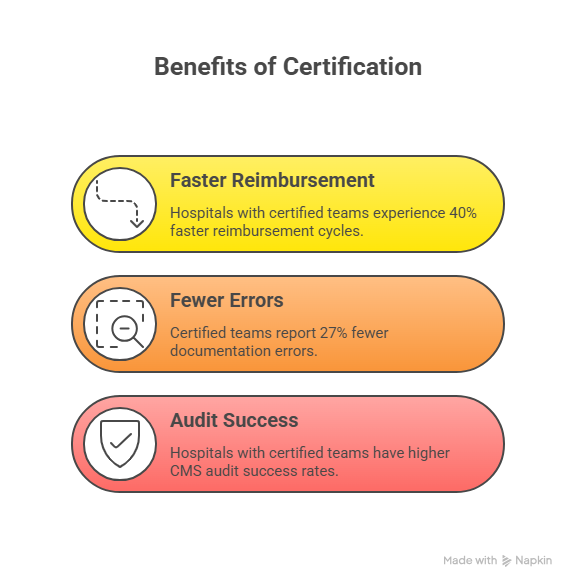
Hospitals employing certified teams have reported:
40% faster reimbursement cycles.
27% fewer documentation errors.
Higher CMS audit success rates.
This evolution mirrors earlier transitions seen in medical scribe certification pathways, where training shifted from optional to mandatory within five years.
Certification is now the professional baseline for administrative credibility.
5. Future Outlook: CMAAs in the Era of AI
CMS’s latest billing reform signals a broader trend — the merger of human expertise and artificial intelligence in administrative healthcare. AI will continue to assist in documentation, but CMAAs remain the final gatekeepers of accuracy.
By 2026, hospitals will expect administrative teams to interpret AI-assisted audit logs, validate machine learning code alignments, and ensure that algorithmic billing matches human-documented data.
Professionals with ACMSO certification are already gaining a competitive advantage in this new landscape, leading hybrid compliance roles that combine coding expertise, audit knowledge, and digital literacy.
The transition may be complex — but it solidifies CMAAs as indispensable players in healthcare’s digital transformation.
6. FAQs: 2025 Billing Code Reforms & CMAA Readiness
-
E/M consolidation, AI documentation codes, and expanded telehealth reimbursement structures.
-
CMAAs are now responsible for auditing AI-assisted records, ensuring modifier accuracy, and verifying time-based claims.
-
Yes — most major providers now require ACMSO CMAA certification or equivalent credentials.
-
EMR interoperability, modifier literacy, telehealth billing, and compliance documentation.
-
Enroll in ACMSO continuing education modules and review real-time CMS updates quarterly.
-
Administrative compliance roles are expected to grow 30% by 2026, driven by automation oversight needs.