Patient Advocacy: Essential Terms & Interactive Role-Play Scenarios
In the evolving landscape of modern healthcare, patient advocacy is no longer optional—it is an essential skill set demanded by hospitals, clinics, and care teams alike. The ability to safeguard patient rights, navigate complex care systems, and ensure patient-centered communication directly correlates with reduced medical errors, improved satisfaction scores, and compliance with regulatory frameworks. Healthcare professionals are now expected to master not just the clinical aspects of care, but also the advocacy competencies that empower patients and families to make informed decisions. Yet, far too many practitioners lack actionable training in this vital area, leaving gaps that compromise outcomes.
This blog doesn’t merely define terms—it brings them to life through practical, interactive role-play scenarios that simulate real-world challenges. By immersing yourself in these cases, you’ll internalize the skills needed to handle breaches of confidentiality, uphold patient autonomy, and navigate insurance denials with confidence. The scenarios are designed to equip you with precise, actionable strategies that translate into immediate clinical practice. Whether you’re a nurse, physician, or allied health professional, this resource delivers the critical, high-impact knowledge you need to advance patient advocacy skills and protect patient rights.
Core Patient Advocacy Terms and Definitions
Understanding Patient Rights and Responsibilities
Patient rights and responsibilities define the essential framework for delivering ethical and effective care. Informed consent isn’t just a signature—it’s a legal and ethical obligation ensuring patients fully understand and agree to proposed treatments. Confidentiality, safeguarded under regulations like HIPAA, protects sensitive health data from unauthorized disclosure. Patient autonomy guarantees that individuals retain control over their medical decisions, even when their choices diverge from medical advice.
On the responsibility side, patients are expected to provide accurate and complete health information, actively participate in their care, and comply with recommended treatments where appropriate. When patients fulfill these roles, it strengthens the patient-provider relationship and supports safe, effective care delivery. Providers, in turn, must honor these rights and encourage responsibilities to create a balanced, trust-driven healthcare environment.
Advocacy vs. Support: Clarifying the Difference
Advocacy is a formalized, structured approach where professionals like patient navigators and ombudsmen step in to represent patient interests, often acting as intermediaries with healthcare systems. Their role is defined, with clear objectives and an understanding of regulatory landscapes. In contrast, support systems—including family members, friends, or community groups—provide emotional and logistical assistance but lack the authority or formal training to handle systemic issues.
Recognizing this distinction is vital. While informal support plays a crucial role in a patient’s well-being, it cannot replace the precise interventions and legal awareness brought by trained advocates. Healthcare professionals must discern when a patient requires emotional support versus when a formal advocate is necessary to resolve disputes, navigate complex systems, or ensure compliance with policies.
Glossary of Essential Advocacy Terms
Case Management: A coordinated process ensuring patients receive timely, appropriate care, including follow-ups and referrals.
Advance Directives: Legal documents outlining patient preferences for care in the event they become incapacitated.
Shared Decision-Making: A collaborative process where clinicians and patients jointly make health decisions, ensuring patient values are central.
Informed Consent: Explicit permission granted by a patient after understanding the risks, benefits, and alternatives of a procedure or treatment.
Pre-Authorization: Insurance requirement where approval must be obtained before a service is delivered to ensure coverage.
Explanation of Benefits (EOB): A document from insurers detailing the services covered, what the insurer pays, and what the patient owes.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): U.S. legislation that protects patient health information privacy and security.
Ombudsman: A trained professional who investigates and resolves complaints in healthcare settings, focusing on patient rights.
Patient Navigator: A guide who helps patients understand the healthcare system, schedule appointments, and access resources.
Continuity of Care: The seamless coordination of healthcare services across providers and time to ensure comprehensive care.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Case Management | A coordinated process ensuring patients receive timely, appropriate care, including follow-ups and referrals. |
| Advance Directives | Legal documents outlining patient preferences for care in the event they become incapacitated. |
| Shared Decision-Making | A collaborative process where clinicians and patients jointly make health decisions, ensuring patient values are central. |
| Informed Consent | Explicit permission granted by a patient after understanding the risks, benefits, and alternatives of a procedure or treatment. |
| Pre-Authorization | Insurance requirement where approval must be obtained before a service is delivered to ensure coverage. |
| Explanation of Benefits (EOB) | A document from insurers detailing the services covered, what the insurer pays, and what the patient owes. |
| HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) | U.S. legislation that protects patient health information privacy and security. |
| Ombudsman | A trained professional who investigates and resolves complaints in healthcare settings, focusing on patient rights. |
| Patient Navigator | A guide who helps patients understand the healthcare system, schedule appointments, and access resources. |
| Continuity of Care | The seamless coordination of healthcare services across providers and time to ensure comprehensive care. |
Interactive Role-Play Scenarios for Mastery
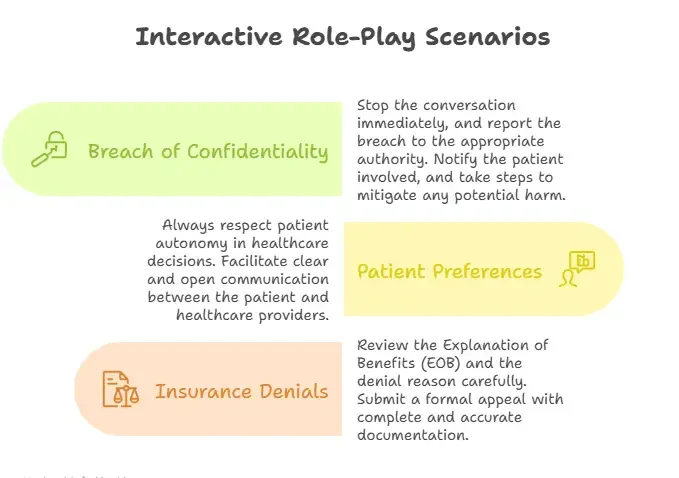
Scenario 1: Handling a Breach of Confidentiality
A nurse inadvertently discusses a patient’s medical condition in a hospital corridor. This conversation is overheard by other patients and staff, leading to a potential breach of confidentiality. An immediate, structured response is crucial. The first step is to acknowledge the breach—this means halting the conversation and moving to a private area. Next, the incident must be reported to the compliance officer or privacy officer within the facility. Document the incident clearly, noting what was disclosed, who overheard it, and how it occurred.
The patient should be informed of the breach in a timely and respectful manner. Apologies should be offered, and a clear outline of steps taken to mitigate harm must be shared. Legal implications under HIPAA may include investigation and sanctions. Ongoing staff training on confidentiality protocols is essential to prevent recurrence. Through this scenario, advocates develop a sharp, actionable approach to safeguarding patient privacy while maintaining trust.
Scenario 2: Advocating for Patient Preferences
A patient with terminal cancer declines further aggressive treatment, preferring palliative care and quality of life over potential extension. The provider is torn between respecting this decision and pursuing treatment options. In this case, the advocate’s role is to facilitate open communication between the patient, family, and medical team. Begin by affirming the patient’s right to autonomy and informed decision-making.
Use reflective listening to clarify patient values, explore concerns, and ensure the decision is based on complete understanding of risks and benefits. Engage in shared decision-making with the care team to align treatment plans with patient preferences. Document all discussions to create a transparent record. This scenario exemplifies how skilled advocacy respects individual choices while maintaining ethical and professional integrity.
Scenario 3: Navigating Complex Insurance Denials
A patient receives a denial for a critical diagnostic procedure due to lack of pre-authorization. The advocate’s first task is to review the Explanation of Benefits (EOB) and denial letter to understand the insurer’s reasoning. Next, gather complete medical documentation and verify whether authorization requirements were communicated properly. Prepare an appeal package, including physician letters, medical necessity documentation, and references to insurer policies.
Submit the appeal within the specified timeframe, ensuring all correspondence is tracked and documented. Communicate clearly with the patient, outlining the appeal process and anticipated outcomes. Follow up with the insurer and escalate if necessary. This scenario equips advocates with the strategic, procedural knowledge to challenge denials effectively, ensuring patients access essential care without undue financial burden.
Skills and Techniques for Effective Patient Advocacy
Active Listening and Empathy
Effective patient advocacy is anchored in active listening—a skill that goes beyond simply hearing. Advocates must demonstrate focused attention, maintaining eye contact and nodding to convey understanding. Techniques such as mirroring, where the advocate reflects back the patient’s words, and summarizing, where key points are restated for clarity, enhance comprehension and rapport. This encourages patients to share concerns openly, fostering a sense of trust and partnership.
Empathy—genuine, heartfelt understanding of another’s experience—transforms conversations. Advocates who listen with empathetic presence validate patient feelings, making them feel valued and respected. By integrating these communication techniques, advocates create an environment where patients are empowered to express their needs, preferences, and fears without reservation. The result is a collaborative, patient-centered approach that strengthens care delivery and outcomes.
Conflict Resolution and Negotiation
In high-stress healthcare settings, conflict is inevitable. Whether disagreements arise between patients and providers or among family members, advocates must be prepared to step in. De-escalation techniques such as maintaining a calm tone, using neutral language, and acknowledging emotions can help defuse tense situations. Reframing, where an issue is presented from a different perspective, often reveals shared goals and facilitates compromise.
Skilled negotiation involves identifying interests, not just positions. Advocates should seek win-win solutions, balancing patient needs with provider or institutional policies. Documenting agreements and ensuring follow-through are critical steps. Mastery of conflict resolution ensures patient voices are heard and respected, even amidst complexity.
Legal and Ethical Awareness
Patient advocacy demands a solid grasp of the legal and ethical landscape. Regulations such as HIPAA dictate strict confidentiality rules, while patient safety laws enforce reporting and quality care standards. Advocates must stay informed about evolving regulations and ethics codes, ensuring compliance and safeguarding patient rights. Ongoing education and participation in professional forums help maintain a sharp, current understanding of legal and ethical frameworks, preventing breaches and reinforcing trust.
| Skill | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Active Listening and Empathy |
- Go beyond hearing; focus attention, maintain eye contact, nod to show understanding. - Use mirroring and summarizing to enhance comprehension and rapport. - Empathetic presence validates patient feelings and fosters open, trusting communication. |
| Conflict Resolution and Negotiation |
- Use de-escalation techniques (calm tone, neutral language, emotion acknowledgment) to manage tension. - Apply reframing to shift perspectives and identify common goals. - Seek win-win solutions, balancing patient needs with policies. - Document agreements and ensure follow-through to maintain trust. |
| Legal and Ethical Awareness |
- Stay informed about HIPAA rules, patient safety laws, and evolving regulations. - Maintain compliance and reinforce ethical practices. - Participate in ongoing education and professional forums to stay updated on legal frameworks. |
How Patient Advocacy Enhances Healthcare Outcomes
Measurable Impacts on Patient Satisfaction and Safety
Strong patient advocacy translates into measurable improvements in healthcare outcomes. Studies show that patients who feel heard and respected report higher satisfaction scores, reduced anxiety, and stronger adherence to treatment plans. Data also indicates that facilities with structured advocacy programs experience fewer adverse events and medical errors, directly enhancing patient safety.
Incorporating shared decision-making and proactive communication into daily practice reduces misunderstandings and fosters collaboration. This approach ensures that patients are informed partners in their care, leading to better management of chronic conditions, fewer hospital readmissions, and improved overall health. Organizations that prioritize advocacy benefit from higher patient engagement, which translates into stronger quality metrics and financial performance.
Aligning with Healthcare Organization Goals
Healthcare organizations are increasingly aligning patient advocacy with strategic goals like reducing readmissions, boosting quality ratings, and improving public trust. Effective advocacy supports these objectives by addressing patient concerns proactively, preventing issues from escalating into formal complaints or legal challenges. When patient voices are integrated into care planning, it cultivates a culture of respect and transparency.
By embedding advocacy into organizational workflows, hospitals and clinics can streamline processes, minimize delays, and ensure that policies reflect patient needs and preferences. This not only enhances care delivery but also strengthens relationships with regulatory bodies and accreditation organizations. A robust advocacy program is no longer a luxury—it’s a strategic imperative that supports patient outcomes and institutional success.
Overcoming Barriers to Effective Patient Advocacy
Fragmentation of Care: Bridging the Gaps
Healthcare settings often suffer from fragmentation of care, where multiple providers manage a patient’s treatment without coordination. Advocates must ensure continuity of care by maintaining accurate documentation, facilitating inter-provider communication, and anticipating potential service gaps that could compromise patient outcomes.
Institutional Resistance: Breaking Through Hierarchies
Some healthcare institutions resist advocacy efforts, with hierarchical structures sidelining patient concerns. Effective advocates leverage a combination of regulatory knowledge, negotiation tactics, and persistence to ensure that patient voices are heard and issues are addressed at the appropriate level. Medical scribes can strengthen this process by ensuring that documentation clearly reflects patient needs and decisions.
Data Privacy and Compliance Challenges
Technology and privacy compliance are complex, and breaches can devastate patient trust. Advocates must navigate EHR systems, enforce HIPAA compliance, and guard patient data. Professionals pursuing the Medical Scribe Certification are equipped with these critical technical skills, ensuring accurate records and patient privacy protection.
Embedding Advocacy in Daily Practice
Advocacy is not an add-on—it must be embedded into daily workflows and institutional culture. Ensuring that policies reflect patient-centered values, creating checklists for proactive intervention, and fostering team-wide commitment to advocacy are all essential. Scribes trained through the Medical Scribe Certification can lead these efforts, positioning themselves as key players in advancing advocacy and compliance excellence.
How ACSMO Trains Scribes to Support Patient Voices—Not Just Capture Their Words
Master Patient Advocacy with Medical Scribe Certification
Patient advocacy is not a skill confined to clinicians—it is a core competency for medical scribes, whose precise documentation and understanding of patient needs are critical to quality care. The Medical Scribe Certification program integrates advocacy principles, ensuring that scribes grasp the importance of patient rights, confidentiality, and the nuances of medical documentation that support fair and ethical treatment. This certification equips scribes with legal awareness, understanding of complex billing systems, and mastery of compliance protocols like HIPAA.
Through this certification, scribes learn to identify and escalate patient concerns, assist providers in shared decision-making, and prevent documentation errors that can compromise care quality. The blog’s scenarios—from handling breaches of confidentiality to navigating insurance challenges—mirror real-world situations scribes encounter daily. By pursuing the Medical Scribe Certification, professionals not only gain credibility but also develop the advocacy skills essential for advancing patient-centered care.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Patient advocacy refers to actions taken by professionals to ensure patients' rights and interests are protected within the healthcare system. It encompasses tasks like navigating complex care systems, ensuring informed consent, and facilitating clear communication between patients and providers. Effective advocacy improves patient satisfaction, enhances treatment adherence, and reduces medical errors. By centering care around the patient’s needs and preferences, advocacy promotes a safer, more ethical healthcare environment. Trained advocates—especially medical scribes—play a pivotal role by ensuring accurate documentation and supporting the patient’s voice throughout the care journey.
-
The Medical Scribe Certification equips professionals with critical skills to support patient advocacy efforts. Certified scribes gain expertise in accurate documentation, regulatory compliance, and patient-centered communication. This training ensures scribes can identify patient concerns, assist providers in shared decision-making, and uphold confidentiality and data protection standards. By understanding both the clinical and administrative aspects of healthcare, certified scribes help bridge gaps in care delivery, reinforce patient rights, and enhance the overall quality of care patients receive.
-
Patient advocates must comply with strict legal frameworks, including HIPAA, informed consent regulations, and patient safety laws. They are responsible for ensuring confidentiality, protecting patient data, and adhering to documentation standards that support legal and ethical requirements. Advocates also play a role in navigating disputes, escalating concerns to appropriate channels, and ensuring accurate recordkeeping. By maintaining compliance with laws and upholding professional integrity, advocates contribute to a safe, ethical, and trustworthy healthcare environment, minimizing risks for both patients and providers.
-
Interactive role-play scenarios provide a dynamic, hands-on approach to mastering advocacy skills. By simulating real-world challenges—like breaches of confidentiality, treatment refusals, or insurance denials—these exercises train professionals to respond effectively under pressure. They foster critical thinking, communication, and negotiation skills, enabling advocates to handle complex situations with confidence. Role-play also helps reinforce legal awareness, empathy, and procedural knowledge. For medical scribes, this training sharpens the ability to document accurately and advocate for patient preferences, making them essential allies in healthcare teams.
-
Medical scribes are instrumental in enhancing patient care by ensuring accurate and timely documentation of medical encounters. This accuracy reduces medical errors, improves care coordination, and supports informed decision-making. Scribes also act as communication bridges between patients and providers, ensuring that concerns are documented and addressed. By alleviating administrative burdens from clinicians, scribes enable providers to focus more on patient interactions, resulting in higher patient satisfaction and improved health outcomes. Certified scribes, in particular, bring specialized skills that align with advocacy goals, further advancing patient-centered care.
-
Overcoming resistance involves a combination of education, persistence, and strategic communication. Advocates must highlight the benefits of patient advocacy for both individuals and healthcare organizations, such as reduced readmissions and improved compliance. Building strong relationships with stakeholders, demonstrating the impact of advocacy through case studies, and leveraging regulatory frameworks to emphasize legal obligations are effective strategies. For medical scribes, integrating accurate documentation and highlighting patient preferences into clinical notes helps reinforce the importance of advocacy, creating a culture that prioritizes patient voices and compliance.
-
Medical scribes uphold confidentiality by adhering to HIPAA standards, utilizing secure EHR systems, and maintaining strict data handling protocols. They must be trained to identify potential privacy breaches, act swiftly to report them, and implement corrective actions. Certified scribes possess specialized knowledge in legal compliance and information security, ensuring that patient data is accurately recorded and protected. Ongoing training, adherence to institutional policies, and vigilance against unauthorized access are essential. This commitment to data privacy fosters patient trust, protects provider reputations, and aligns with ethical healthcare standards.
-
The future of patient advocacy and medical scribe roles lies in increased integration of technology, data analytics, and patient-centered care models. Scribes will be expected to manage complex data, navigate advanced EHR systems, and support providers in delivering personalized, value-based care. Advocacy will expand to include proactive engagement in population health initiatives, addressing social determinants of health, and influencing policy changes. Certified medical scribes who master these evolving demands will be crucial in driving improved outcomes, reducing disparities, and ensuring that healthcare remains responsive to diverse patient needs.
Summing Up: Key Advocacy Skills & Takeaways
Mastering patient advocacy isn’t just an added skill—it’s a necessity in modern healthcare. By internalizing core concepts like informed consent, confidentiality, and autonomy, and practicing with realistic role-play scenarios, you can strengthen your ability to navigate complex patient needs. These skills not only enhance patient satisfaction and safety but also align with organizational goals, ensuring you stand out as a leader in healthcare environments.
Whether you’re an experienced provider, an aspiring advocate, or pursuing the Medical Scribe Certification, this knowledge positions you for success. Now is the time to invest in developing your advocacy skills—because when patients are heard and protected, everyone wins.
| Interactive Poll: Which Scenario Do You Find Most Challenging? | |
|---|---|