HIPAA Simplified: Everything Medical Admin Assistants Need to Know
In the evolving landscape of healthcare privacy and security, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) stands as a cornerstone regulation. For medical administrative assistants, understanding HIPAA is non-negotiable—not just as a compliance formality but as a core responsibility. HIPAA mandates the protection of Protected Health Information (PHI), safeguarding patient data from unauthorized access, misuse, and breaches. Medical administrative assistants are often the first point of contact for patients and, consequently, the first line of defense for data security.
Missteps—whether through careless handling of digital records, improper verbal disclosures, or lax workstation security—can lead to significant legal liabilities and erode patient trust. Mastery of HIPAA’s principles is vital to ensure both regulatory compliance and a seamless patient experience. This guide distills HIPAA into clear, actionable insights tailored specifically for medical admin assistants. We’ll explore the key components of HIPAA, practical protocols for daily tasks, strategies for avoiding common mistakes, and the value of certification and training in today’s high-stakes healthcare environment.
Understanding HIPAA – The Basics
What is HIPAA?
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), enacted in 1996, is a federal regulation designed to safeguard Protected Health Information (PHI). It was introduced to improve healthcare coverage portability, but its most recognized contribution is establishing national standards for data privacy and security. HIPAA applies to healthcare providers, health plans, and clearinghouses, collectively termed as covered entities, as well as business associates handling PHI. For medical administrative assistants, understanding HIPAA is fundamental to professional integrity and compliance obligations.
PHI includes names, addresses, dates of birth, social security numbers, and medical records—any data that can identify a patient. Mishandling PHI can result in severe penalties, both civil and criminal, and erode public trust. HIPAA’s main objective is to limit PHI disclosure to only necessary uses and to empower patients with rights over their data. For instance, patients can request access to their records, request corrections, and control who views their information. Medical admin staff play a crucial role in ensuring these rights are honored while maintaining efficient workflows. By mastering HIPAA’s foundational principles, medical admin assistants position themselves as vital safeguards of patient data, reducing legal risks for their organizations and reinforcing patient confidence in the healthcare system.
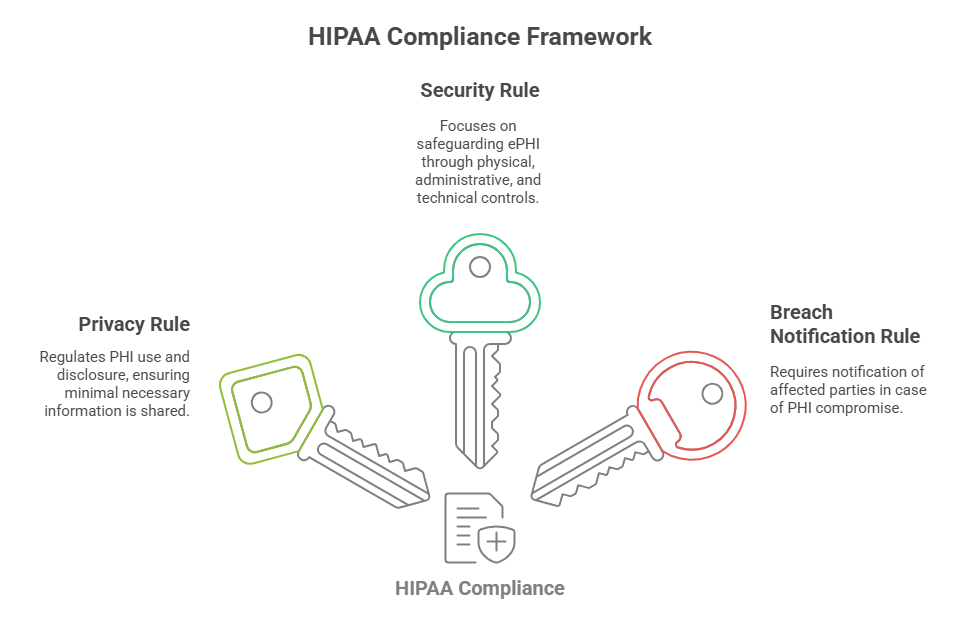
Key Components of HIPAA
HIPAA is composed of three primary rules that directly impact daily administrative tasks: the Privacy Rule, the Security Rule, and the Breach Notification Rule. The Privacy Rule sets limits on how PHI can be used or disclosed. It mandates that only the minimum necessary information is shared for specific purposes, such as treatment, payment, and healthcare operations. Medical administrative assistants must ensure that verbal disclosures at the front desk, electronic communications, and record handling comply with these standards. The Security Rule focuses on electronic PHI (ePHI), requiring physical, administrative, and technical safeguards. This includes password protections, encryption, and controlled access to digital records.
Admin assistants must be vigilant with email communications, ensuring PHI is only transmitted securely and accessed by authorized personnel. The Breach Notification Rule outlines procedures for responding to a data breach. If PHI is compromised, covered entities must notify affected individuals, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and, in some cases, the media. Admin staff play a key role in identifying and reporting breaches quickly and accurately. Together, these HIPAA components create a comprehensive framework that protects patient data, mitigates risks, and reinforces the trustworthiness of healthcare organizations.
Core Responsibilities of Medical Admin Assistants
Handling Patient Information
Medical administrative assistants are responsible for the secure management of PHI throughout a patient’s journey—from scheduling to discharge. Best practices for handling patient information include verifying identities before disclosing records, maintaining organized filing systems, and limiting access to authorized personnel.
When managing digital records, assistants should use encrypted systems and follow password protocols to ensure PHI is only accessible to those with a need-to-know basis. Avoiding unauthorized access includes logging off workstations when unattended and regularly updating passwords. Front desk staff should keep computer screens angled away from public view, and paper records should be filed in locked cabinets.
Records management extends to sharing information with external providers. When faxing PHI, assistants should use pre-programmed numbers to avoid misdirected transmissions, attach confidentiality cover sheets, and confirm receipt with the intended recipient. For emails, encrypted channels and secure portals should be used, avoiding personal email systems altogether.
These practices not only comply with HIPAA but also reinforce patient trust. A medical office where patients feel their information is safe builds loyalty and reduces the risk of legal repercussions.
Communication and Consent
HIPAA mandates clear protocols for verbal and written communications about PHI. Medical admin assistants must verify patient identity through multiple points—such as name, date of birth, and address—before disclosing information. When taking phone calls, assistants should avoid discussing PHI in public areas, even if a caller is verified.
Consent is crucial. Assistants must obtain written authorization before sharing information with third parties, including family members not listed on the patient’s consent forms. Each consent document should clearly state the information disclosed, the purpose, and an expiration date if applicable. These documents must be stored securely, either digitally with encryption or in locked physical files.
For routine communications, like appointment reminders or lab results, practices must establish policies ensuring minimum necessary disclosures. This might include leaving voicemail messages without sensitive details or using secure messaging portals. When patients request records, medical admin assistants should provide them promptly, following the practice’s established process and verifying identity before releasing any information.
By mastering these protocols, assistants ensure legal compliance and demonstrate a commitment to patient care and privacy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several pitfalls can jeopardize HIPAA compliance in daily admin tasks. Common mistakes include:
Leaving patient charts or files visible in open areas.
Faxing PHI to incorrect numbers due to manual entry errors.
Discussing patient information within earshot of unauthorized individuals.
Sharing passwords or leaving workstations unlocked.
Avoiding these errors requires constant vigilance and reinforcement through training, ensuring that patient privacy remains protected at every interaction.
HIPAA Compliance in Daily Practice
Secure Data Handling
Electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) is central to healthcare administration, and secure data handling is non-negotiable for medical administrative assistants. Using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and encrypted systems helps prevent unauthorized access. Passwords must be unique and updated frequently, and systems should enforce auto-logout after inactivity.
Email communication requires heightened vigilance. Assistants should use encrypted email services, avoid transmitting PHI through personal accounts, and confirm recipient identities before sending sensitive data. Even with internal emails, sharing minimum necessary information minimizes risks. When printing PHI, assistants must collect documents immediately and dispose of unneeded records via secure shredding.
Digital storage solutions—whether cloud-based or on-site servers—must comply with HIPAA’s technical safeguard standards. This includes firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems. Medical admin staff should also maintain a record of system access logs to track any unauthorized attempts or irregular activities.
By enforcing these practices, medical admin assistants not only comply with regulations but also establish themselves as trusted stewards of patient data.
Physical Security and Access
Securing physical workspaces is as critical as digital protection. Medical admin assistants must ensure that PHI—whether in files, on screens, or in other media—is protected from unauthorized access. This includes locking file cabinets, controlling office entry points, and using privacy screens for computer monitors.
Workstations should be strategically positioned to prevent visual breaches, and access to records rooms should be restricted to authorized personnel only. Visitor access must be controlled with sign-in protocols and escort policies. Paper records should be stored in locked cabinets, and keys or combinations should be kept secure.
Shredding is a non-negotiable step in disposing of outdated PHI. Assistants must use cross-cut shredders and verify complete destruction before disposal. Portable devices, like laptops and USB drives containing PHI, should be stored securely when not in use and encrypted to protect data in transit.
Routine audits of physical security protocols help identify potential vulnerabilities and reinforce compliance. Medical admin assistants are the gatekeepers of both digital and physical health information, ensuring compliance across every touchpoint.
Handling Breaches and Incidents
Despite robust protocols, breaches can occur. Medical admin assistants must recognize and respond swiftly to incidents involving PHI. If a breach is suspected—whether from a misplaced file, unauthorized access, or a phishing attempt—it must be reported immediately to the designated compliance officer.
Documentation of the incident, including details of the breach, individuals affected, and actions taken, is crucial for regulatory reporting. Fast and accurate reporting not only helps mitigate damage but also demonstrates the organization’s commitment to HIPAA compliance and patient trust.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Secure Data Handling |
Use strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and encrypted systems. Update passwords frequently and auto-logout after inactivity. Use encrypted email and confirm recipients before sending PHI. Collect printed documents promptly and use secure shredding. Ensure digital storage meets HIPAA technical safeguards (firewalls, antivirus, intrusion detection). Maintain access logs to monitor system usage. |
| Physical Security and Access |
Lock file cabinets, control office entry, and use privacy screens. Position workstations to prevent visual breaches. Restrict access to records rooms to authorized personnel. Control visitor access with sign-ins and escort protocols. Use cross-cut shredders for paper disposal and secure portable devices. Conduct routine audits of physical security protocols. |
| Handling Breaches and Incidents |
Recognize and report breaches immediately to compliance officer. Document details of breaches, affected individuals, and actions taken. Prompt and accurate reporting mitigates damage and demonstrates commitment to HIPAA compliance. |
HIPAA Training and Certification for Admin Assistants
Importance of Certification
Formal HIPAA training and certification are essential for medical administrative assistants aiming to navigate the complex landscape of healthcare data privacy and security. Certification ensures assistants gain a comprehensive understanding of HIPAA requirements, enabling them to handle Protected Health Information (PHI) responsibly and lawfully.
Certified staff demonstrate a commitment to compliance and best practices, which builds trust with patients and employers alike. Healthcare providers are increasingly prioritizing HIPAA-compliant staff because violations can result in penalties up to $1.5 million per year, reputational damage, and patient distrust. Medical admin assistants who proactively pursue certification stand out as trusted, knowledgeable professionals capable of protecting sensitive data.
HIPAA-certified assistants are equipped to interpret privacy and security rules, identify risks, and implement mitigation strategies. Certification also emphasizes incident response planning—a crucial skill for managing breaches effectively. Beyond personal competency, certification fosters a culture of compliance and accountability, reducing the likelihood of costly errors in medical office operations.
In an era where digital health records and cyber threats are increasingly prevalent, HIPAA training is more than a checkbox—it’s a strategic investment in a secure, patient-centered practice.
Recommended Training Programs
Our HIPAA compliance training course offers comprehensive modules that prepare medical admin assistants to handle real-world scenarios. The curriculum covers:
Privacy Policies: Detailed breakdowns of the Privacy Rule, emphasizing appropriate use and disclosure of PHI.
Security Protocols: Practical guides for implementing technical, physical, and administrative safeguards, including encryption, secure access controls, and workstation best practices.
Case Studies: Realistic scenarios highlighting common compliance challenges, such as misdirected faxes, unauthorized disclosures, and data breaches.
Incident Response: Step-by-step procedures for identifying, reporting, and mitigating potential breaches.
The course is designed for busy professionals, offering flexible online modules that can be completed at one’s own pace. Participants receive certificates of completion, enhancing their resumes and credibility in healthcare roles. Training is continually updated to reflect regulatory changes, ensuring assistants stay ahead of evolving compliance standards.
Completing a recognized HIPAA certification program isn’t just a personal milestone; it’s a strategic advantage that demonstrates dedication to privacy protection and regulatory excellence. Assistants who invest in their compliance knowledge not only safeguard patients but also position themselves for career advancement and increased professional value.
Summing Up: The Takeaway
For medical administrative assistants, mastering HIPAA compliance is more than a legal obligation—it’s a strategic imperative. By understanding and implementing HIPAA’s privacy, security, and breach notification rules, assistants become pivotal in safeguarding Protected Health Information (PHI). Their expertise ensures not only legal compliance but also strengthens patient trust and supports a seamless healthcare experience. Investing in HIPAA training and certification equips medical admin staff with practical skills to manage daily tasks confidently, identify risks, and handle breaches effectively. With evolving threats and increasing reliance on digital health records, having HIPAA-certified staff is a competitive advantage for any healthcare organization.
This guide has outlined the core responsibilities, best practices, and essential training avenues that empower medical administrative assistants to excel in data privacy and security management. By adhering to these standards, assistants demonstrate professional integrity and contribute to a culture of compliance and patient care excellence. Explore our HIPAA training course today to strengthen your compliance skills, protect your organization, and advance your career in healthcare administration.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
HIPAA, or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, is a U.S. federal law designed to protect Protected Health Information (PHI) and ensure patient privacy. In a medical office setting, HIPAA compliance is critical because administrative staff frequently handle sensitive data during scheduling, billing, and communications. Failure to follow HIPAA regulations can result in hefty fines, legal action, and loss of patient trust. By safeguarding PHI, medical offices protect patients’ personal and health information, foster trust, and demonstrate commitment to compliance and ethical standards. Staff must be trained to manage PHI responsibly and avoid inadvertent breaches, ensuring the integrity of healthcare operations.
-
HIPAA protects any data that can identify a patient and is related to their health, treatment, or payment. This includes names, addresses, dates of birth, social security numbers, insurance details, and medical records. Even conversations or notes containing patient identifiers are considered Protected Health Information (PHI). Administrative assistants must recognize that both electronic and paper records, as well as verbal communications, fall under HIPAA’s scope. Ensuring that this information is stored securely, accessed only by authorized personnel, and shared with minimal disclosure is essential. Failing to protect PHI can result in serious penalties and jeopardize the organization’s reputation and compliance.
-
Medical admin assistants can ensure HIPAA compliance by adopting secure data management protocols. This includes verifying patient identities, using encrypted email systems, ensuring workstations are locked when unattended, and limiting access to PHI. Assistants should regularly update passwords, avoid using personal devices for work-related data, and use confidential cover sheets when faxing PHI. Verbal communications must be discreet, ensuring patient details are not overheard. Staff should also stay current with HIPAA training, reinforcing their knowledge of regulations and best practices. Following these steps demonstrates commitment to data protection, builds patient trust, and mitigates legal risks.
-
HIPAA violations can have severe consequences, including fines ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with a maximum of $1.5 million per year for multiple infractions. Individual staff may face disciplinary action, including termination, and in extreme cases, criminal charges. Violations damage the reputation of healthcare facilities, resulting in lost patient trust and potential lawsuits. Organizations may be subject to corrective action plans (CAPs) imposed by regulatory bodies. For administrative assistants, even unintentional breaches—such as misdirected faxes or unsecure emails—can have serious repercussions. Adhering to HIPAA protocols protects both staff and facilities from these risks.
-
While HIPAA does not mandate specific training for administrative assistants, the law requires that all employees with access to PHI receive training on HIPAA compliance. Most healthcare organizations implement formal training programs that cover privacy rules, security protocols, and breach response procedures. Many offer certification opportunities, which enhance credibility and ensure staff are well-prepared to manage PHI securely. Regular training updates are essential to keep staff informed about evolving regulations and best practices. Completing HIPAA training not only fulfills legal requirements but also reinforces a culture of compliance, professionalism, and patient-centered care in medical offices