How to Prepare for the Certified Medical Assistant Certification Exam
Becoming a Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) opens the door to a rewarding career in healthcare. As the demand for medical assistants continues to grow, obtaining this certification from a recognized authority like the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA) or the American Medical Technologists (AMT) enhances your job prospects and professional credibility. But how should you prepare for the CMA exam? In this blog, we will explore the exam structure, key study topics, the best study materials, and tips to succeed in your certification exam.
Overview of the Exam Structure
Before diving into study materials and resources, it’s essential to understand the exam structure for the Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) certification. The CMA exam is typically administered by two major organizations: the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA) and American Medical Technologists (AMT). While both organizations offer certification exams for medical assistants, the exams differ slightly in format, but their core goal remains the same: to assess the candidate’s knowledge and skills needed to perform the essential duties of a medical assistant in a clinical or administrative capacity.
AAMA Certification Exam Structure
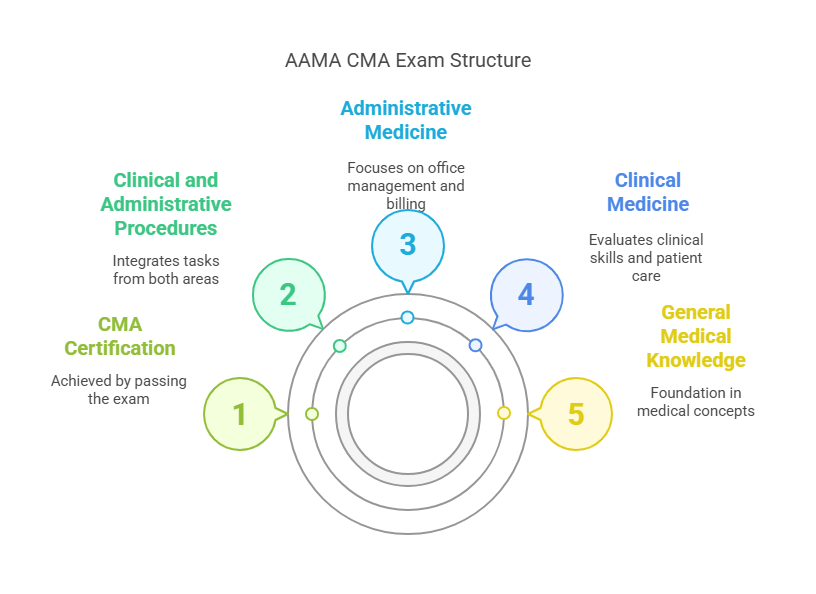
The AAMA CMA exam is designed to evaluate the candidate’s proficiency in medical assisting across multiple areas. The exam consists of 200 multiple-choice questions, which are strategically divided into four major domains. Each domain focuses on a different aspect of the medical assistant's role in healthcare, ensuring that a comprehensive skillset is tested.
General Medical Knowledge (25%) This section assesses your foundational understanding of medical terminology, anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology. Understanding these key areas is essential for identifying medical conditions, performing diagnostic tests, and communicating with healthcare teams and patients. A solid grasp of general medical knowledge forms the bedrock of your ability to assist in patient care effectively. You’ll also be tested on the essential concepts related to human biology, organ systems, and their interdependencies.
Clinical Medicine (40%) The bulk of the AAMA CMA exam focuses on clinical procedures, infection control, and patient care. This section covers practical skills such as taking vital signs, performing diagnostic tests, administering injections, assisting in medical exams, and managing infection control protocols. Knowledge in patient interaction and ensuring their safety while undergoing treatment is key to passing this section. Clinical Medicine questions evaluate your preparedness to assist physicians and other healthcare professionals in a variety of clinical tasks and ensure proper patient care.
Administrative Medicine (15%) As a medical assistant, administrative duties are just as crucial as clinical tasks. This domain tests your knowledge of medical office management, billing and coding, and understanding insurance processes. Being proficient in administrative duties such as scheduling appointments, handling patient records, and maintaining confidentiality is fundamental to ensuring that the medical office runs smoothly. This section also emphasizes the importance of understanding medical insurance forms, claims submission, and coding systems like ICD-10 and CPT.
Clinical and Administrative Procedures (20%) The final section combines elements of both clinical and administrative functions. Questions in this category focus on interdisciplinary tasks, where you may need to demonstrate knowledge in areas like patient intake, handling medical records, and performing clinical assessments. This domain emphasizes your ability to switch seamlessly between clinical and administrative duties, a common requirement in many healthcare settings.
Candidates are given 160 minutes (approximately 2 hours and 40 minutes) to complete the entire exam. The passing score for the AAMA CMA exam is typically 430 out of 800, though the exact score required may vary slightly depending on the exam’s difficulty level. This score range ensures that only candidates with a sufficient level of competency in all tested areas can earn the prestigious CMA certification.
Understanding the structure of the CMA exam is crucial to planning your study strategy effectively. By knowing the distribution of topics and allocating study time accordingly, you can ensure that you are well-prepared to succeed in obtaining your CMA certification.
AMT Certification Exam Structure
The AMT certification exam, also known as the Registered Medical Assistant (RMA) exam, is a comprehensive test designed to assess a candidate’s readiness to work as a medical assistant in a variety of healthcare settings. The exam consists of 210 multiple-choice questions that are strategically divided into several key categories. These categories cover both clinical and administrative aspects of medical assisting, ensuring that candidates possess a well-rounded skill set to perform their duties effectively.
The exam is broken down into the following major categories:
General Medical Assistant Procedures (20%) This section evaluates your ability to perform essential general medical assistant tasks. These tasks may include patient intake, preparing patients for examinations, taking vital signs, and ensuring the clinical environment is well-organized and safe for patients. A solid foundation in medical terminology, anatomy, and patient care protocols is essential for this category.
Clinical Procedures (30%) Clinical procedures focus on your ability to perform tasks in direct patient care. This category covers skills such as administering injections, preparing for diagnostic tests, assisting with physical exams, and managing patient records. It also includes infection control procedures and ensuring patient safety during medical procedures.
Laboratory and Diagnostic Procedures (20%) This section tests your knowledge and skills related to laboratory tests, diagnostic equipment, and procedures. Candidates must be familiar with tasks such as performing blood draws, preparing specimens for testing, and understanding laboratory results to assist healthcare providers in diagnosing patients.
Pharmacology and Medications (15%) Understanding medications, dosage calculations, drug interactions, and the safe administration of drugs is critical for medical assistants. This section assesses your knowledge of pharmacology, including commonly prescribed medications and their potential side effects.
Medical Law and Ethics (15%) Ethical considerations and legal responsibilities are essential in the medical field. This section covers topics like patient confidentiality, informed consent, and professional conduct. Understanding HIPAA, patient rights, and medical ethics is crucial for this category.
The AMT exam lasts 2 hours and 30 minutes, and while the passing score can vary, it generally falls within the range of 70% to 75%. The exam is designed to ensure that candidates have a practical understanding of the broad range of tasks they will perform in a medical setting.
While both the AAMA and AMT exams share similarities, such as the inclusion of clinical and administrative knowledge, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the specific format of the exam you are pursuing. By understanding the structure, you can create a tailored study plan that helps you focus on the areas most relevant to your certification goals.
Key Study Topics for the CMA Exam
The Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) exam covers a broad spectrum of topics that assess both clinical and administrative knowledge. To ensure success, you need to be well-prepared in all areas tested on the exam. Below, we break down the key study topics that will help you focus your preparation efforts and ensure you are equipped to handle the diverse duties required of a medical assistant.
Clinical Knowledge
The clinical section of the CMA exam tests your ability to provide direct patient care. As a medical assistant, your role will often involve interacting with patients, taking medical histories, and assisting healthcare professionals in various clinical settings. Below are the critical clinical study topics to focus on:
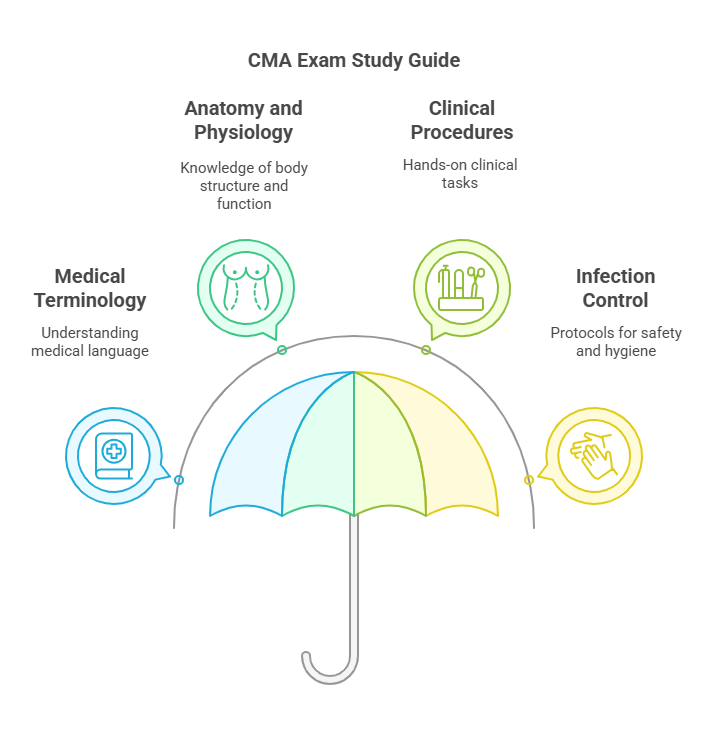
a. Medical Terminology
Understanding medical terminology is fundamental to your success as a medical assistant. You must become fluent in the language of medicine, as it is used to describe medical conditions, procedures, and anatomy. This knowledge will allow you to communicate effectively with doctors, nurses, and patients. Key areas to focus on include prefixes, suffixes, root words, and medical abbreviations. Familiarity with terminology helps you interpret medical charts, lab results, and patient histories accurately.
b. Anatomy and Physiology
A strong understanding of anatomy and physiology is essential. This area of study focuses on the structure and function of the human body. You will need to know the systems of the body (e.g., cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems), how they function, and how they interrelate. A deep understanding of human anatomy and physiology will allow you to better assist physicians and other healthcare providers during patient examinations, diagnostic testing, and treatment.
c. Clinical Procedures
This category includes the hands-on clinical tasks you’ll perform regularly as a medical assistant. You must be prepared to demonstrate proficiency in areas such as:
Patient intake: Gathering important medical history and vital signs from patients before they see a physician.
Taking vital signs: This includes measuring blood pressure, temperature, pulse, and respiratory rate to monitor the patient’s overall health.
Administering injections: You must be familiar with the proper techniques for giving vaccinations, blood draws, and other injections.
Minor medical procedures: Tasks such as assisting in wound care, applying dressings, and removing sutures may be required.
d. Infection Control
Knowledge of infection control protocols is critical in a healthcare setting to ensure the safety of both patients and staff. This includes understanding sterilization and disinfection methods, proper hand hygiene, and maintaining a clean and sterile environment. You will also need to understand personal protective equipment (PPE) and standard precautions to prevent the spread of infections, particularly in a clinical setting.
Administrative Knowledge
Medical assistants don’t just perform clinical tasks; they are also responsible for a variety of administrative functions that are vital to the smooth operation of a medical practice. Here are the key areas to focus on for administrative knowledge:
a. Medical Office Management
In this role, you will be managing multiple tasks that keep the office organized and functioning. Key tasks include:
Managing appointments: Scheduling patient visits, managing calendars, and making reminders for follow-up appointments.
Maintaining patient records: Ensuring all patient information is accurate, up-to-date, and stored securely in compliance with regulations.
Managing office procedures: Handling phone calls, assisting in patient intake, processing forms, and ensuring the office runs efficiently.
b. Medical Billing and Coding
As a medical assistant, you will often be responsible for billing and coding. This is a vital aspect of the healthcare system, as it ensures that healthcare providers are paid for their services. You must understand:
CPT codes: These codes describe medical, surgical, and diagnostic services.
ICD-10 codes: These are used to describe the diagnoses or conditions a patient is being treated for.
Insurance claims: How to prepare and submit claims to insurance companies to receive reimbursements for services rendered.
Reimbursement process: Understanding how the healthcare reimbursement system works, including the types of insurance plans and coverage options.
c. Health Insurance
Familiarity with the health insurance landscape is crucial. You should be able to:
Differentiate between types of insurance plans (e.g., HMO, PPO, Medicaid, Medicare).
Understand the claims process: Learn how to submit claims and ensure proper payment.
Understand coverage options: Recognize the various types of coverage and the benefits that come with each.
d. Medical Law and Ethics
Medical assistants must adhere to strict ethical and legal standards. Familiarize yourself with:
Patient rights: Understanding informed consent and patient autonomy.
Confidentiality (HIPAA): The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) protects patient privacy. Medical assistants must understand how to safeguard sensitive patient information.
Ethical medical practices: Maintaining a high standard of care and ensuring patient safety in every aspect of practice.
Ethics and Professionalism
In addition to clinical and administrative skills, medical assistants must maintain the highest standards of professionalism and ethical conduct. The ability to interact with patients, families, and healthcare professionals in a compassionate and respectful manner is crucial. Here are key ethical principles to focus on:
a. Patient Confidentiality
Medical assistants are responsible for safeguarding patient information. Familiarize yourself with HIPAA regulations to ensure you’re following appropriate procedures for handling, storing, and sharing patient records.
b. Informed Consent
Informed consent is a foundational principle in medical ethics. As a medical assistant, you should understand the process by which patients give their consent for medical procedures and treatments, ensuring they fully understand what will happen and any risks involved.
c. Non-Bias Approach in Patient Care
Maintaining a non-bias approach in patient care is essential. Treating all patients with respect, regardless of their background, beliefs, or conditions, is a core principle in healthcare. Developing cultural sensitivity and understanding patient needs will help you foster positive relationships with patients and healthcare teams.
Best Study Materials and Resources for CMA Exam Preparation
Preparing for the Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) exam can feel overwhelming due to the breadth of knowledge required. However, selecting the right study materials and utilizing the best resources can make all the difference. Below is an expanded list of some of the most effective study tools, textbooks, and resources available to help you succeed in passing the CMA exam.
Textbooks and Guides
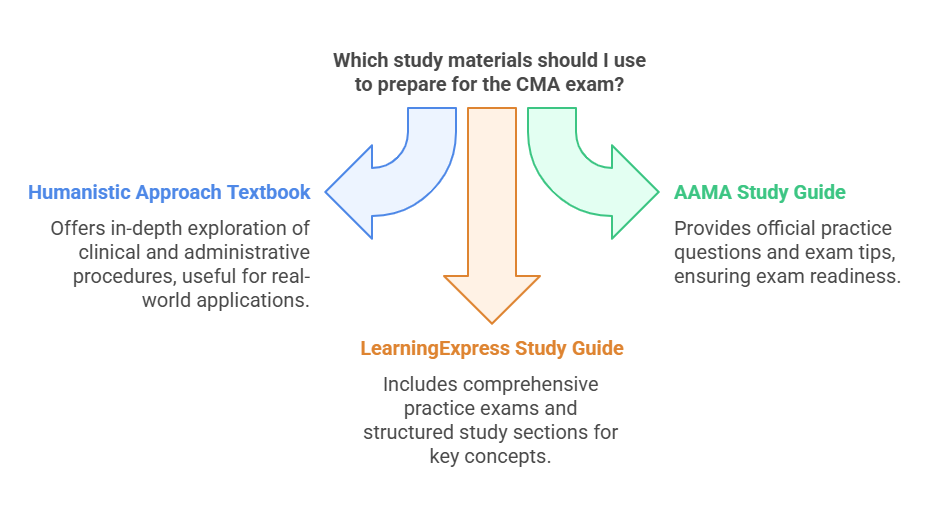
a. "Medical Assisting: A Humanistic Approach" by Judi L. Nath and Julie S. Daugherty
This textbook offers an in-depth exploration of both clinical and administrative procedures in the field of medical assisting. The book is especially useful for understanding the real-world applications of your knowledge, making it easier to apply what you’ve learned in practice. It covers a variety of topics, from patient care to the day-to-day office procedures essential for running a healthcare practice efficiently.
b. "CMA Exam Study Guide" by the AAMA
The American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA) provides an official study guide tailored specifically to the CMA exam. This guide includes practice questions, review materials, and exam tips, ensuring you are well-prepared for the types of questions you will face on the exam. AAMA's resources are designed by the very organization that administers the CMA exam, so they offer reliable and current information.
c. "The Medical Assistant Exam Study Guide" by LearningExpress
This comprehensive study guide offers practice exams and study materials that align with the full CMA exam structure. It covers everything from general knowledge to clinical and administrative skills. It is particularly helpful for reviewing key concepts, as it offers structured study sections with explanations and additional tips to tackle difficult subjects.
Online Study Resources
a. AAMA Online Study Resources
AAMA offers online study resources that include online courses, practice tests, and exam prep materials. These resources are specifically designed to help you prepare for the CMA exam. Since these materials are curated by AAMA, they provide targeted preparation that aligns with the structure and content of the CMA exam, making them one of the best resources available.
b. Quizlet
Quizlet is a versatile tool that allows you to study using flashcards based on CMA exam topics. You can search for existing flashcard sets or create your own to focus on areas where you need more practice. This tool is especially useful for memorizing terms, definitions, and medical terminology that are key to the CMA exam. The flashcard format makes learning active and engaging.
c. MedPreps
MedPreps offers a comprehensive set of practice questions and full-length practice exams that simulate the real testing environment. This platform is designed to help you become familiar with the structure of the exam and test your knowledge under timed conditions. It is a great way to gauge your readiness and pinpoint any weak areas that need further study.
d. Mometrix Test Preparation
Mometrix offers a detailed study guide and a series of practice tests that cover every aspect of the CMA exam. Their materials focus on both clinical and administrative knowledge, offering test-taking strategies, exam tips, and a wide range of questions to practice. Mometrix is highly regarded for its structured approach and depth of content, making it a great resource for thorough preparation.
Mobile Apps
a. CMA Test Prep App (AAMA)
The CMA Test Prep App from the American Association of Medical Assistants is the official app for preparing for the CMA exam. This app includes practice questions and test strategies that will help you study effectively on the go. The app is specifically designed to simulate the real CMA exam environment and provides a portable way to study.
b. MedAssistant Exam App
This interactive app is an excellent tool for preparing for the CMA exam. It offers flashcards and practice quizzes that help reinforce what you’ve learned. The MedAssistant Exam app focuses on essential clinical and administrative topics and allows you to track your progress over time, ensuring you remain on track with your study plan.
Recommended Study Schedule
Creating a study schedule and sticking to it is one of the most effective ways to stay organized and avoid last-minute cramming. Below is a suggested schedule to guide your study plan for the months leading up to your exam.
Month 1: Review Fundamentals
During the first month of preparation, focus on building a strong foundation in general medical knowledge. Study anatomy, medical terminology, and basic physiology. This is the time to familiarize yourself with the fundamental concepts that will appear throughout the exam. In addition to textbooks, consider watching educational videos on platforms like YouTube to enhance your understanding.
Month 2: Focus on Clinical Knowledge
In the second month, transition into studying more specialized clinical procedures and patient care. Focus on understanding infection control protocols, clinical examinations, and medical procedures such as injections and wound care. Start taking practice quizzes regularly to assess your knowledge and identify areas that need improvement.
Month 3: Administrative and Ethics
The third month should be dedicated to administrative tasks and medical law and ethics. Study topics such as medical billing, coding, patient rights, and confidentiality. Ethical considerations, such as maintaining patient privacy and informed consent, should be studied in-depth as well.
Final Week: Practice Mock Exams
In the final week, take full-length practice exams under timed conditions to simulate the actual test day. This is your chance to fine-tune your time management skills and work on areas where you feel less confident. Focus particularly on the sections where you scored the lowest in previous practice tests.
Practice Questions and Mock Tests
Practice is critical to doing well on the CMA exam. The more questions you answer, the more confident you will become in tackling the exam's various sections.
Use platforms like Quizlet or MedPreps to take multiple practice exams.
Simulate test conditions by taking timed mock exams to improve your ability to manage your time and reduce anxiety.
Review the questions you answered incorrectly and make sure you understand why the correct answer is right. This review process helps reinforce your knowledge and prepares you to tackle similar questions on the exam.
Conclusion
Preparing for the Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) exam requires dedication, focus, and the right resources. By understanding the exam structure, covering key study topics, and using the best study materials, you can position yourself for success. Remember to take practice exams, follow a structured study schedule, and use tips from certified professionals to maximize your preparation.
At ACMSO, we offer Medical Scribe Certifications that can complement your CMA preparation and boost your career in the healthcare field.
Lesser-Known Facts About CMA Certification
The AAMA (American Association of Medical Assistants) is the only nationally recognized certifying body for Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) exams, ensuring credibility and uniform standards in the healthcare industry. Visit the official AAMA site.
A CMA credential is valid for five years, after which professionals must renew by completing continuing education requirements or retaking the exam. Learn more.
CMA exam fees are often reimbursed by employers, especially those offering professional development or healthcare certification support programs to their staff. Details here.
Some states offer a medical assistant license in addition to national certification, which may expand clinical responsibilities and job opportunities locally. State-specific info.
The AAMA offers exclusive discounts on exam prep materials, such as study guides, webinars, and flashcards, to support members preparing. Member benefits.
Many hospitals require CMA certification to meet staffing quality standards, ensuring patient care is delivered by qualified and trusted professionals. Certification importance.
A CMA certification often leads to better pay, with salary increases between 10%-15%, depending on role, location, and experience. Wage insights.
The AAMA CMA exam is available in English and Spanish, making it more accessible to candidates from bilingual or multicultural backgrounds. Exam overview.
CMAs can specialize in various areas, such as cardiology, geriatrics, and pediatrics, by gaining further clinical experience and targeted training. Career paths.
The AMT (American Medical Technologists) also certifies allied health professionals in fields like radiology, phlebotomy, and medical lab tech. Explore AMT.
FAQs
-
The AAMA CMA certification exam focuses on general medical knowledge, clinical procedures, and administrative knowledge, whereas AMT's RMA exam includes a wider range of topics, including diagnostic procedures and medical law.
-
It's recommended to begin studying at least 3 months before the exam date, dedicating about 10-15 hours per week.
-
Yes, the AAMA and AMT both offer remote proctoring options for the exam, allowing you to take it from home.
-
The passing score is typically 430 out of 800 for AAMA, and around 70-75% for AMT exams.
-
Many medical assistant programs and organizations, including the AAMA, offer scholarships or financial assistance for exam preparation.